
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Light Field Manipulation and Information Acquisition, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, School of Physical Science and Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710129, China
2 Research & Development Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical University in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518063, China
3 Key Laboratory of Photonic Technology for Integrated Sensing and Communication, Ministry of Education, and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Information Photonics Technology, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
4 Institute of Fluid Physics, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
5 e-mail: zbren@nwpu.edu.cn
6 e-mail: jiangleidi@gdut.edu.cn
7 e-mail: jlzhao@nwpu.edu.cn
The time-delay problem, which is introduced by the response time of hardware for correction, is a critical and non-ignorable problem of adaptive optics (AO) systems. It will result in significant wavefront correction errors while turbulence changes severely or system responses slowly. Predictive AO is proposed to alleviate the time-delay problem for more accurate and stable corrections in the real time-varying atmosphere. However, the existing prediction approaches either lack the ability to extract non-linear temporal features, or overlook the authenticity of spatial features during prediction, leading to poor robustness in generalization. Here, we propose a mixed graph neural network (MGNN) for spatiotemporal wavefront prediction. The MGNN introduces the Zernike polynomial and takes its inherent covariance matrix as physical constraints. It takes advantage of conventional convolutional layers and graph convolutional layers for temporal feature catch and spatial feature analysis, respectively. In particular, the graph constraints from the covariance matrix and the weight learning of the transformation matrix promote the establishment of a realistic internal spatial pattern from limited data. Furthermore, its prediction accuracy and robustness to varying unknown turbulences, including the generalization from simulation to experiment, are all discussed and verified. In experimental verification, the MGNN trained with simulated data can achieve an approximate effect of that trained with real turbulence. By comparing it with two conventional methods, the demonstrated performance of the proposed method is superior to the conventional AO in terms of root mean square error (RMS). With the prediction of the MGNN, the mean and standard deviation of RMS in the conventional AO are reduced by 54.2% and 58.6% at most, respectively. The stable prediction performance makes it suitable for wavefront predictive correction in astronomical observation, laser communication, and microscopic imaging.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(11): 1802
1 辽宁工程技术大学 测绘与地理科学学院,辽宁 阜新 123000
2 黑龙江地理信息工程院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150081
对比仅包含多光谱信息、仅可实现二维土地覆盖分类的传统光学遥感数据,机载多光谱激光雷达(multispectral light detection and ranging,MS-LiDAR)的优势在于同时包含多光谱和空间信息、可实现三维土地覆盖分类,但现有的机载MS-LiDAR数据的土地覆盖分类研究所需特征维度过高、算法复杂度高。因此,提出了一种整合空间相关性和归一化差分比率指数(Normalized Difference Ratio Index,NDRI)特征的逐步分类算法。该算法首先融合机载MS-LiDAR数据的多波段独立点云,获取兼具空间位置及其多光谱信息的单一点云数据;然后利用空间邻域增长下的地面滤波算法分离地面和非地面点;接着基于不同目标的激光反射特性差异设计将草地(树木)自地面(非地面)中分离的NDRI指数,并利用类间方差最大原则下的自适应最优NDRI指数实现地面和非地面点的精细分类;最后利用3D多数投票法优化分类结果。采用加拿大Optech Titan实测MS-LiDAR数据测试提出算法的有效性及可行性,实验结果表明:算法的平均总体精度和Kappa系数分别可达90.17%和0.861,可有效实现城区MS-LiDAR数据的三维土地覆盖分类;分步处理的方式更有利于针对具体的分离目标的特点设计简单且有效的规则,算法设计更简单、复杂度低;NDRI可为其他机器学习算法的显著性特征的设计和选择提供理论支撑。
机载多光谱激光雷达 点云分类 三维土地覆盖分类 归一化差分比率指数 滤波 airborne multispectral lidar point cloud classification 3D land cover classification normalized difference ratio index filtering 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(2): 20220376
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrumentation and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
2 CASTECH Inc., Fuzhou 350003, China
3 National Engineering Laboratory of Special Display Technology, National Key Laboratory of Advanced Display Technology, Academy of Photoelectric Technology, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
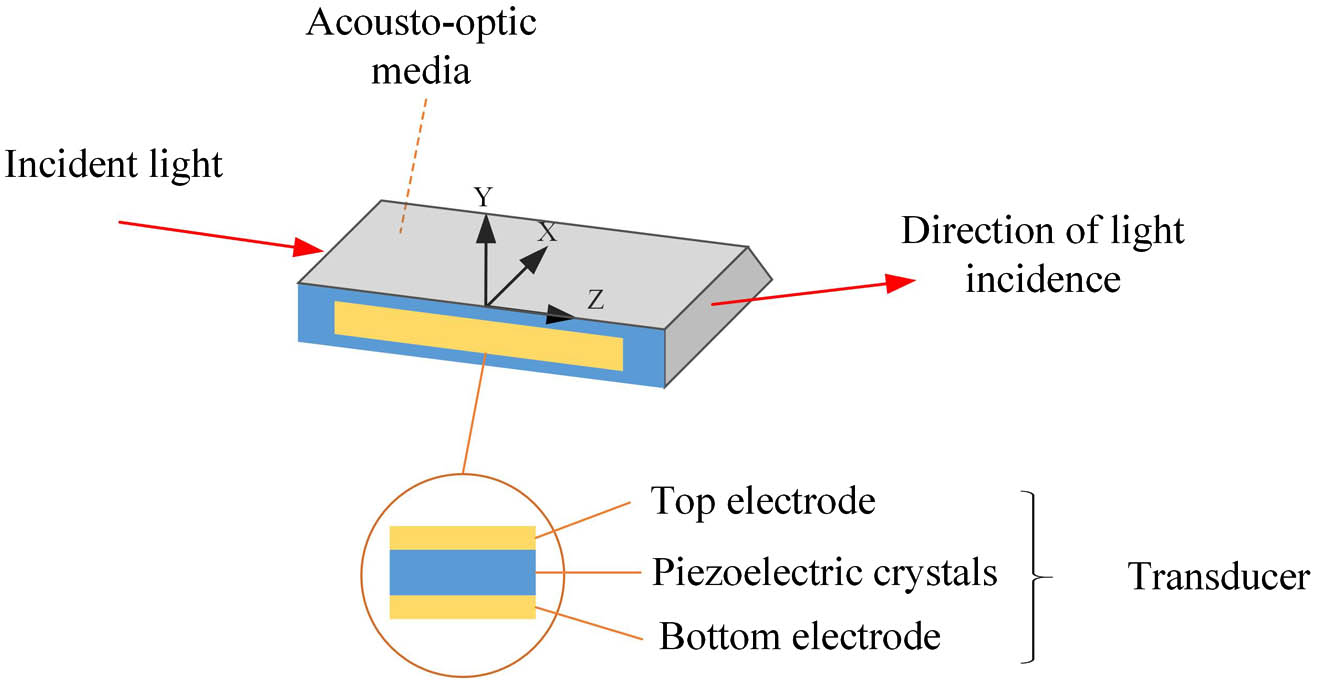
In an acousto-optic modulator, the electrode shape plays an important role in performance, since it affects the distribution of the acoustic field. The acousto-optic modulator based on the conventional rectangular electrode has the problems of low energy efficiency and small modulation bandwidth due to an imperfect acoustic field. In this paper, a new serrated periodic electrode has been proposed for using acousto-optic modulator transducers. The proposed electrode has the following advantages. By using serrated periodic electrodes to suppress the sidelobes, the collimation of the acoustic field in the direction perpendicular to the light incidence is improved. This makes the acousto-optic modulator have a stable diffraction efficiency fluctuation and high energy efficiency. In addition, the electrode has a large divergence angle in the direction of light incidence, so a large bandwidth can be obtained. The simulations and experiments demonstrate that the serrated periodic electrode has an increased bandwidth and high energy efficiency.
acousto-optic modulator serrated periodic electrode large bandwidth low power consumption Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(3): 031403
1 光场调控与信息感知工业和信息化部重点实验室, 西北工业大学, 陕西 西安 710129
2 陕西省光信息技术重点实验室, 西北工业大学物理科学与技术学院, 陕西 西安 710129
近年来,深度学习技术的爆发式发展引领了机器学习的又一次浪潮。深度神经网络具备抽象特征的高效识别与提取能力、强大的非线性拟合能力、抗干扰鲁棒性及非凡的泛化能力,被广泛应用于自动驾驶、目标识别、机器翻译、语音识别等领域。最近几年,卷积神经网络(CNN)在光学信息处理中获得广泛应用,本文介绍CNN的基础概念和结构构成,回顾其在数字全息术、条纹分析、相位解包裹、鬼成像、傅里叶叠层成像、超分辨显微成像、散射介质成像、光学层析成像等领域的最新应用进展,评述CNN在光学信息处理中的典型应用特点,最后分析CNN应用于光学信息处理中的不足,并展望其未来发展。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(16): 1600001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Physical Electronics and Devices of the Ministry of Education & Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Information Photonic Technique, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
The quantum multimode of correlated fields is essential for future quantum-correlated imaging. Here we investigate multimode properties theoretically and experimentally for the parametric amplified multiwave mixing process. The multimode behavior of the signals in our system stems from spatial phase mismatching caused by frequency resonant linewidth. In the spatial domain, we observe the emission rings with an uneven distribution of photon intensity in the parametric amplified four-wave mixing process, suggesting different spatial modes. The symmetrical distribution of spatial spots indicates the spatial correlation between the Stokes and anti-Stokes signals. While in the frequency domain, the multimode character is reflected as multiple peaks splitting in the signals’ spectrum. A novelty in our experiment, the number of multimodes both in the spatial and frequency domains can be controlled by dressing lasers by modifying the nonlinear susceptibility. Finally, we extend the multimode properties to the multiwave mixing process. The results can be applied in quantum imaging.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(12): 12001454
1 清华大学 精密仪器系 精密测试技术及仪器国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
2 北京航空航天大学 仪器科学与光电工程学院, 北京 100191
3 福建福晶科技股份有限公司, 福建 福州 350003
准确的双折射特性测量对于液晶的实际应用具有重要意义。研究了液晶材料的工作原理, 以激光回馈效应为基础, 搭建了各向异性外腔回馈双折射测量系统, 对不同驱动电压下液晶的双折射特性进行测量。测量结果表明, 各向异性外腔回馈双折射测量系统测量精度在0.3°之内; 通过施加0~24V交流电压, 液晶材料双折射率在2.74×10-1~2.39×10-3范围内变化, 对应各向异性呈现出460°~5°的大范围位相延迟值。电压范围在0.7~2V时, 电压-双折射率关系表现出较好的线性度, 通过线性拟合对该范围内电压-双折射率关系进行计算, 其线性度优于95.5%。液晶材料可以提供稳定的位相延迟, 同一电压值下的位相延迟短期重复性优于0.52°, 长期重复性优于4.5°。
液晶材料 双折射特性 位相延迟 激光回馈效应 各向异性外腔回馈 liquid crystals birefringence phase retardation laser feedback effect anisotropy external cavity feedback 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(3): 0306003
1 中国科学院国家空间科学中心 微波遥感重点实验室, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
通过特殊设计的高精度SMMW器件, 实现了一套基于二单元干涉仪的干涉式辐射计系统.针对该系统的自身特点, 作者提出了点源目标响应定标方法来降低系统误差.系统完成后, 分别进行了干涉条纹实验和点源目标成像实验.经测试, 系统的线性相位误差小于2°, 角分辨率优于0.57°.系统实测性能和理论分析结果一致.以上研究为今后设计高分辨率亚毫米波干涉式成像辐射计提供了重要的参考价值.
亚毫米波成像 点源目标响应定标 亚毫米波干涉条纹 干涉式成像 submillimeter-wave (SMMW) imaging point-source calibration SMMW interference fringes interferometric imaging
1 中国卫星海上测控部, 江苏 江阴 214431
2 西安交通大学理学院, 陕西 西安 710049
3 西安工程大学理学院, 陕西 西安 710048
金属纳米材料因其表面等离子体共振特性而备受关注。 异质结构的金属纳米材料的光学特性相比于同质结构因其材料的不同破坏了原有结构的对称性, 对称性的破坏将引起光学性质的改变, 相邻两个颗粒之间的相互作用会产生Fano共振。 Fano共振是由异质纳米结构的表面等离子体共振耦合引起的, 通过合理地调控表面等离子体共振的耦合, 将进一步调控Fano共振的强度同时促使异质结构的电场增强特性和辐射特性得到进一步优化。 受金银等贵金属的带间跃迁影响, 金属铝纳米材料成为研究紫外-近紫外光区的表面等离子体共振研究最佳选择。 采用有限时域差分方法研究了Ag-Al纳米球二聚体的光学特性。 研究了Ag和Al纳米球组成的二聚体的吸收光谱与入射光偏振方向、 纳米球半径、 颗粒间距和介质折射率等几何结构及物理参数的关系, 并深入讨论了二聚体的局域场分布规律; 讨论了获取更高效的Fano共振光谱的方法。 由于材料的对称性被破坏, 异质二聚体的光学性质与同质二聚体明显不同, Ag-Al异质纳米球二聚体呈现出在紫外和可见光区的双Fano共振现象。 Ag-Al二聚体表面等离子体互相耦合引起Fano共振从而导致表面等离子体的共振抑制和增强。 研究结果对在紫外-可见光区的表面等离子体应用、 纳米光学器件的设计与开发及基于表面等离子体共振的表面增强光谱、 生物传感和检测研究等有一定参考价值。
Ag-Al纳米球二聚体 时域有限差分方法(FDTD) 局域表面等离子体共振(LSPR) Fano共振 Silver-aluminum nanosphere heterodimer Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) theory Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) Fano resonance 光谱学与光谱分析
2016, 36(11): 3470
1 College of Resources and Environment, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan430070, China
2 School of Agriculture and Food Systems, Faculty of Land and Food, the University of Melbourne, Horsham, Victoria3401, Australia
3 Institution of Soil and Fertilizer, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hefei230031, China
4 International Plant Nutrition Institute, China Program, Wuhan430074, China
5 Agricultural and Technical Center, Datonghu Administration District of Honghu City, Honghu434300, China
光谱学与光谱分析
2011, 31(9): 2555
1 福建师范大学物理与光电信息科技学院, 福建 福州 350007
2 福建师范大学化学与材料学院, 福建 福州 350007
双钨酸盐晶体Nd∶NaGd(WO4)2(简称Nd∶NGW)和Nd∶NaLa(WO4)2(简称Nd∶NLW)是一类新出现的比较有前途的激光晶体, 它们属于四方晶系白钨矿结构。根据对称性分类,用商群理论分析了两种晶体的拉曼光谱。此类钨酸盐晶体一个原胞中理论上有36个振动模。使用半导体激光的785 nm波长和Ar +激光的514.5 nm激发, 测得激光光入射方向分别垂直和平行于光轴方向的偏振拉曼光谱(100~2000 cm-1), 并对测得的拉曼峰进行了指认。由于Nd3+离子进入晶体取代离子的半径不同,晶格对Nd3+跃迁影响大小不同, Nd∶NGW和Nd∶NLW的拉曼光谱也表现出了差异性。通过不同激发波长的拉曼谱的比较, 在中间波段发现并确认了几个共振拉曼峰。
材料 激光晶体 共振拉曼 拉曼光谱 双钨酸盐





